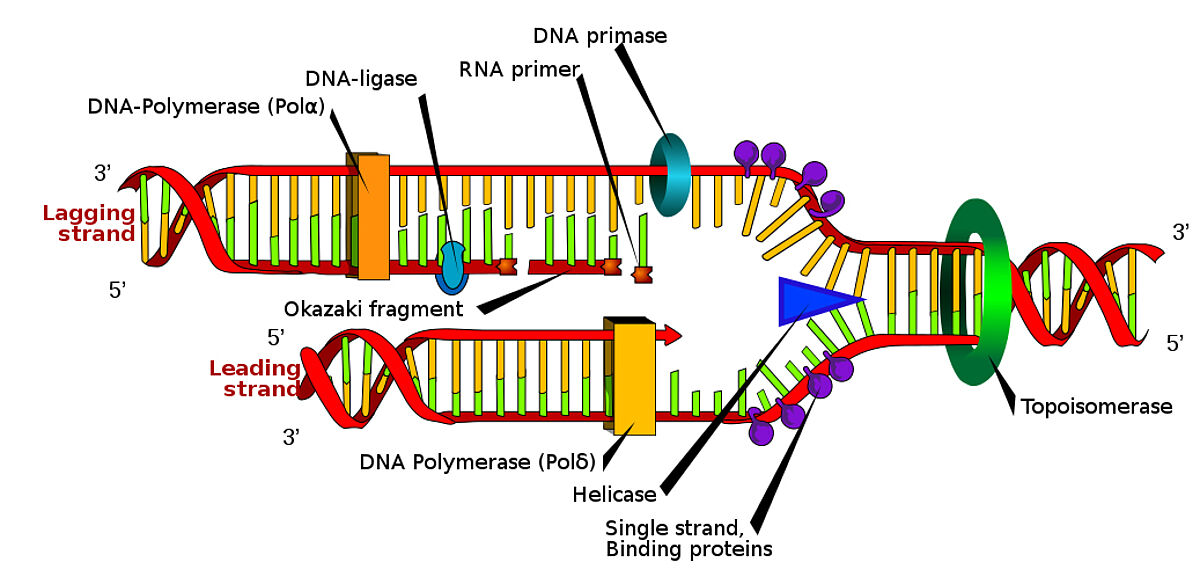
Ligases, DNA polymerases, and RNA polymerases molecular biology enzymes with distrinct functions and applications:
Ligases: Ligases are enzymes that catalyze the formation of phosphodiester bonds between DNA or RNA molecules. They are responsible for joining fragmented DNA strands, repairing DNA damage, and connecting DNA or RNA molecules. Ligases play a crucial role in sealing the nicks or gaps in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA or RNA, ensuring the continuity and integrity of genetic material.
DNA Polymerases: DNA polymerases are enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of new DNA strands by adding complementary nucleotides to a DNA template strand during DNA replication and repair. They work in a highly accurate and processive manner, ensuring faithful duplication of DNA. DNA polymerases also have proofreading mechanisms to correct errors that may occur during DNA synthesis, contributing to their crucial role in maintaining genomic stability.
RNA Polymerases: RNA polymerases are enzymes responsible for transcribing DNA sequences into complementary RNA strands. During transcription, RNA polymerases recognize specific DNA sequences known as promoters and initiate the synthesis of RNA molecules from a DNA template. There are different types of RNA polymerases in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, each responsible for synthesizing different classes of RNA, such as mRNA (messenger RNA), rRNA (ribosomal RNA), and tRNA (transfer RNA). RNA polymerases play a vital role in gene expression, as they are involved in producing the templates for protein synthesis.
DNA Polymerase
Bst DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus
Bst DNA Polymerase, Exonuclease Minus,* is a recombinant form of the 67 kDa Bacillus stearothermophilus DNA Polymerase protein (large fragment). The enzyme has 5′→3′ polymerase activity and strand-displacement activity, but it lacks 3′→5′ exonuclease activity. It also has reverse transcription activity.
- Strand-displacement amplification
- DNA sequencing through high GC regions
- Rapid sequencing from nanogram amounts of DNA template
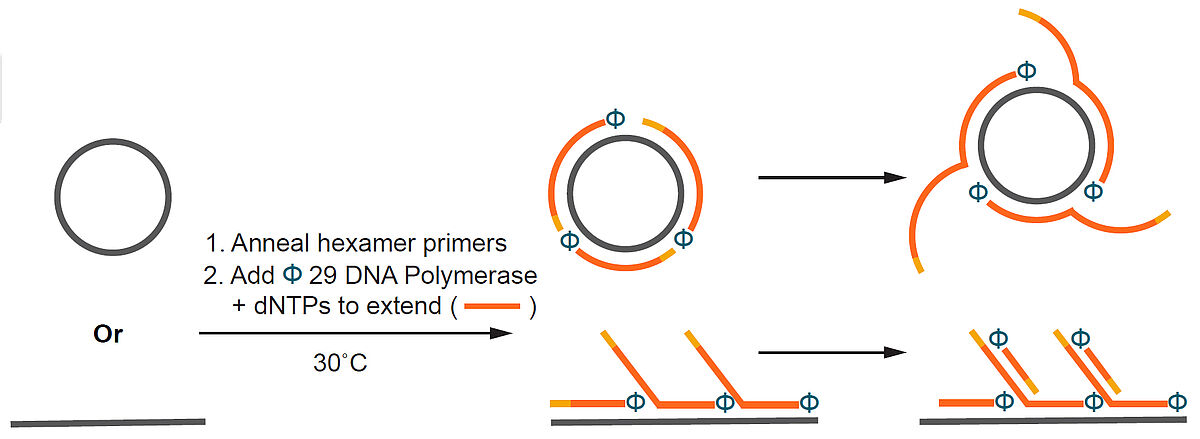
NxGen phi29 DNA Polymerase
NxGen phi29 DNA Polymerase (φ29 DNA Polymerase) is a highly processive enzyme with exceptional strand-displacement activity. The enzyme also contains a 3′→5′ exonuclease activity that enables proofreading capability
Exo-Minus Klenow DNA Polymerase (D355A, E357A)
Exo-Minus Klenow DNA Polymerase is a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase that lacks both the 5′→3′ and 3′→5′exonuclease activities of E. coli DNA Polymerase I, from which it is derived. This N-terminal truncation of DNA Polymerase I also has two mutations (D355A and E357A).
- Random-primer labeling of DNA
- Second-strand cDNA synthesis
- Strand-displacement amplification
FailSafe Enzyme Mix
FailSafe Enzyme Mix is a unique blend of thermostable DNA polymerase and a 3′→5′ proofreading exonuclease that is capable of amplifying most difficult templates. The FailSafe enzyme provides 3-fold higher fidelity than Taq DNA polymerase, with the ability to amplify PCR products up to 20 kb. The error rate of the FailSafe Enzyme Mix is approximately 1 in 27,000–30,000.
- PCR and multiplex PCR
- PCR of difficult templates
- High-sensitivity PCR
- PCR amplification of any sequence up to 20 kb
EconoTaq DNA Polymerase
Derived from Thermus aquaticus, this enzyme has optimal activity at temperatures above 70 °C. It has an intrinsic 5′→3′ structure-dependent exonuclease activity but lacks 3′→5′ proofreading exonuclease activity. EconoTaq’s low price is coupled with high quality and performance. It is supplied with a magnesium-containing buffer or a separate tube of MgCl2.
- PCR and multiplex PCR amplification of DNA templates
EconoTaq PLUS 2X Master Mix
EconoTaq PLUS 2X Master Mix is a ready-to-use PCR master mix, containing dNTPs and PCR Enhancer. It offers outstanding performance and value, and is perfect for routine PCR.
- PCR and multiplex PCR amplification of DNA templates
MasterAmp Tth DNA Polymerase
This recombinant enzyme from Thermus thermophilus has DNA polymerase activities up to ~95 °C, as well as reverse-transcriptase activity. High reaction temperatures can reduce nonspecific priming and template secondary structure. It is provided with MasterAmp PCR Enhancer.
- PCR amplification of DNA
- Improved PCR of DNA templates having a high degree of secondary structure
- One-step RT-PCR of RNA
RNA Polymerase
NxGen T7 RNA Polymerase
T7 RNA Polymerase catalyses the 5′→3′ RNA synthesis from the T7 promoter. It is a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase cloned from the T7 bacteriophage. It recognises the T7 promoter and terminator sequences with high specificity.
- Synthesis of RNA for nucleic acid amplification methods or gene expression studies
Poly(A) Polymerase Tailing Kit
Poly(A) Polymerase uses ATP as a substrate for template-independent addition of adenosine monophosphate to the 3′-OH termini of RNA molecules. The Poly(A) Polymerase Tailing Kit provides the enzyme and other reagents for quickly and easily adding a poly(A) tail to the 3′ end of any RNA.
- Addition of a poly(A) tail to RNA synthesised in vitro
- Synthesis of polyadenylated RNA for nucleic acid amplification methods or gene expression studies
- 3′-end-labeling of RNA with radioactive A residues
T7 R&DNA Polymerase
This enzyme is a mutant form of T7 RNA polymerase (Y639F mutant). The mutation enables T7 R&DNA Polymerase to incorporate 2′-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) into full-length “RNA” transcripts more efficiently than the corresponding wild-type T7 RNA polymerase.
- This mutant enzyme uses the same T7 transcription promoters as the wild-type T7 RNA polymerase.
- Synthesis of “RNA” transcripts of mixed rNMP/2′-dNMP composition
- Synthesis of modified “RNA” transcripts that are resistant to RNase A