Introduction
If a DNA donor template is supplied along with the CRISPR components, knock-in of a desired sequence can be achieved via the homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway. The donor template contains the sequence of interest (knock-in sequence) flanked by sequences that are homologous to the target genomic sequence (homology arms). Because a defined template is used, HDR is typically accurate and the sequence of interest is inserted into the genome seamlessly. However, HDR only occurs in the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is less efficient than non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Efficiencies around 20% may be achieved but the outcome strongly depends on the cell type used.
In general, a high HDR rate is key to efficiently achieving gene knock-ins utilizing a CRISPR system and following the HDR approach. LubioScience offers high-quality HDR donor DNAs from our trusted supplier Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT). IDT's HDR donors contain chemical modifications that can help improve stability and overall HDR rates. The donors can easily be designed with the Alt-R HDR Design Tool, which is provided by IDT. Furthermore, we offer HDR Enhancer V2, a small molecule compound that blocks NHEJ, effectively tilting the balance of repair pathways in favor of HDR.
Donor DNAs for HDR
For donor DNA, researchers frequently use a single- or double-stranded DNA sequence. The choice of ssDNA or dsDNA depends largely on the size of the insertion, and the ability to synthesize a donor of the required length. When you are designing the HDR donor template, differentiating between small indels/mutations and long insertions is helpful. Our supplier IDT recommends the following:
| Small mutations and short insertions: Use Alt-R HDR Donor Oligos that include two flanking homology arms (30–60 nt each) and your insertion/mutation sequence (maximum template length is 200 nt). |
| Mid-length insertions: Use HDR Donor Blocks that include two flanking homology arms (100–400 bp each) and your insertion sequence (maximum template length is 3000 bp). Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are linear dsDNA fragments containing chemical modifications designed to improve HDR and reduce unintended blunt integrations. |
| Very long (greater than ~2500 nt) insertions: Use plasmids or linearized plasmids containing your homology arms (generally at least 500 nt) and sequence of interest, but monitor the cells for toxicity. Use of circular dsDNA with a minimal plasmid backbone, such as Nanoplasmids, may help improve HDR when toxicity is a limiting factor. |
The Alt-R HDR Design Tool is very helpful for designing HDR Donor Oligos and HDR Donor Blocks.
Alt-R™ HDR Donor Oligos
Alt-R™ HDR Donor Oligos are single-stranded DNA oligos for HDR produced by IDT's proprietary synthesis process under ISO 9001 standards. These high-quality oligos are up to 200 bases long and ideal for introducing point mutations or short insertions. Alt-R HDR Donor Oligos are available in tube or plate formats. We provide different options for researchers to select from, depending on the specific needs of their application:
- No modification: standard DNA
- PS modification: 4 phosphorothioate bonds: 5′–N*N*NNN…NNN*N*N–3′, where * represents a PS bond and N represents a DNA base
- Alt-R HDR modification: IDT’s proprietary modification pattern developed through extensive testing to increase donor oligo stability and enable the highest rate of repair
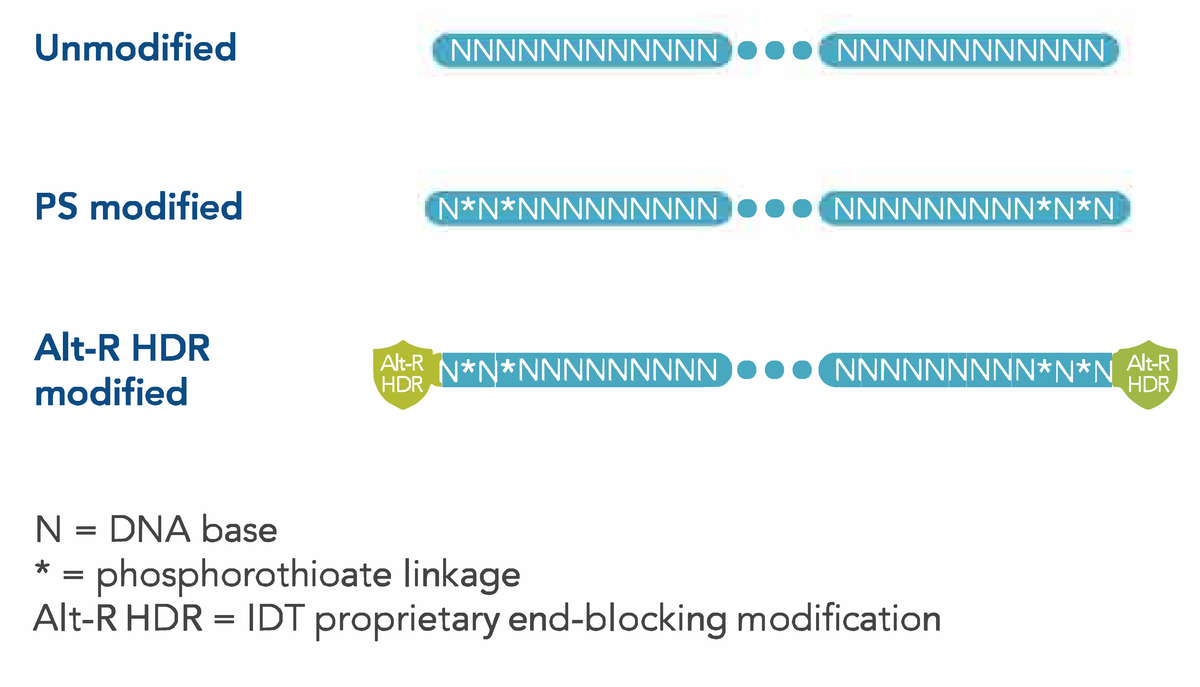
Phosphorothioate linkages at the 5’ and 3’ ends of a short ssDNA donor act as stabilizing modifications that protect the donor from exonuclease activity. This protection means that more DNA is available for insertion, especially in cells such as iPS and Jurkat cells, which have high levels of nucleases. Another improvement to HDR donor DNA is the addition of the IDT proprietary Alt-R modification, which further stabilizes the donor ssDNA, greatly increasing HDR.
Alt-R™ HDR Donor Blocks
For researchers looking to accelerate their CRISPR, HDR-mediated insertions (>120 bases), IDT's dsDNA templates offer a cost-effective, high-fidelity option to reduce the amount of downstream screening via higher HDR rates and lower unintended integrations. The HDR Donor Blocks incorporate advanced chemical modifications at each end of the sequence to boost HDR rates and aid in inhibiting the occurrence of blunt-end integration of the donor sequence. In addition, universal sequences are added to the ends of the sequence ordered to provide consistency and speed of production. Alt-R HDR Donor Blocks are available from 201 to 3000 bases in length and are generated from clonally purified DNA. The donors are sequence-verified via next-generation sequencing and are composed of A, T, G, and C nucleotides only.
The Alt-R™ HDR Design Tool
If you don’t have a template design of your own, use our Alt-R HDR Design Tool to design your template. Simply provide basic information about your target site, and then use the tool to design and visualize your desired edit within the sequence. The Alt-R HDR Design Tool will provide the recommended HDR donor template along with gRNA(s) for your specifications. It enables greatly increased HDR rates by providing optimized donor template design and Cas9 guide RNA selection. The higher HDR rates result from clear design rules based on extensive wet-bench testing and customer validation. You can use the tool by entering a gene name, accession number, genomic coordinates, or sequence in FASTA format for multiple species, including human, mouse, rat, zebrafish, and nematode. The tool also supports custom designs, as well as single, or multiple, entries.
Alt-R™ HDR Enhancer V2
The IDT Alt-R HDR Enhancer V2 is a small molecule compound which blocks NHEJ, effectively tilting the balance of repair pathways in favor of HDR. The Alt-R HDR Enhancer can be used with either Cas9 or Cas12a systems and works in multiple cell lines. The enhancer is provided as a 0.69 mM concentrated solution in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Workflow overview of an HDR experiment
1 | This step only applies to Cas9 experiments using a 2-part guide RNA: Mix the crRNA and tracrRNA together to form the guide RNA. Heat and slowly cool to form an annealed gRNA complex. |
2 | Mix the Cas enzyme with the guide RNA (when using Cas12a, this is only the crRNA) to form the RNP complex. |
3 | Deliver the RNP complex and HDR donor to the cells or model organism. |
4 | Allow the cells to incubate and grow (often this takes about 24–48 hours, depending on the cell type). During this time, cells may be incubated with HDR Enhancer V2 for 12–24 hours to boost the rates of HDR. |
5 | Analyze the samples to determine the success of your genome editing. |
Documents
Take a look at our revised application note on the optimization of HDR in mammalian cell lines to explore the following:
- Criteria for selecting guide RNA sequences
- Considerations on the rational design of synthetic DNA donor templates
- Details on how to optimize every step in your experiment for more efficient HDR outcomes
For more general information about CRISPR genome editing, please refer to IDT's CRISPR basics handbook.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing, IDT does not intend for these products to be used in clinical applications and does not warrant their fitness or suitability for any clinical diagnostic use. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations.

