How do you deliver guide RNA and Cas enzyme into cells?
There are several methods for delivering CRISPR components into cells: electroporation or transfection (lipofection) of either actual reagents or plasmids encoding the reagents, microinjection, and viral vectors encoding the reagents. It is now widely accepted that the safest delivery method for CRISPR is to bind the Cas enzyme to the gRNA outside of the cell and deliver it as a complete RNP. The reason is that if you use a plasmid or viral vector, the plasmid or vector stays in the cells longer than an RNP complex does. This means the CRISPR components are produced continually over a period of time, increasing the risk of triggering an immune response or off-target editing of the genome.
The two techniques usually used to deliver RNP into cells are electroporation and lipofection. Microinjection is a less common method used primarily in oocytes or embryos, although electroporation has successfully been used in embryos too. In most non-embryo experiments, you will choose between electroporation and lipofection. Electroporation generally requires higher RNP concentrations (2–4 μM RNP) than lipofection (often as low as 10 nM RNP). We usually recommend electroporation over lipofection for most experiments.
Our supplier Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) offers potent electroporation enhancers for the delivery of CRISPR RNPs into cells. They also provide a large number of protocols to help you establish optimal experimental conditions for successful RNP delivery. Read further to discover more information about these topics.
Delivery via electroporation
Electroporation uses a short pulse of electrical current to increase cell permeability temporarily, allowing molecules to be delivered into the cell. Researchers at IDT recommend that you test a range of RNP concentrations before your experiment, starting with the concentrations suggested in their protocols, to establish optimal electroporation conditions for the experimental cell line, as well as help maximize cell viability. We sell positive and negative control guide RNAs that are useful for these optimization experiments.
Electroporation devices successfully used with IDT reagents and a wide variety of cell types include instruments from Bex, Lonza (Nucleofector system), Thermo Fisher Scientific (Neon system), Nepa Gene, and Bio-Rad (Gene Pulser™ Xcell™ system). There are many IDT-verified and/or user-submitted protocols using these instruments.
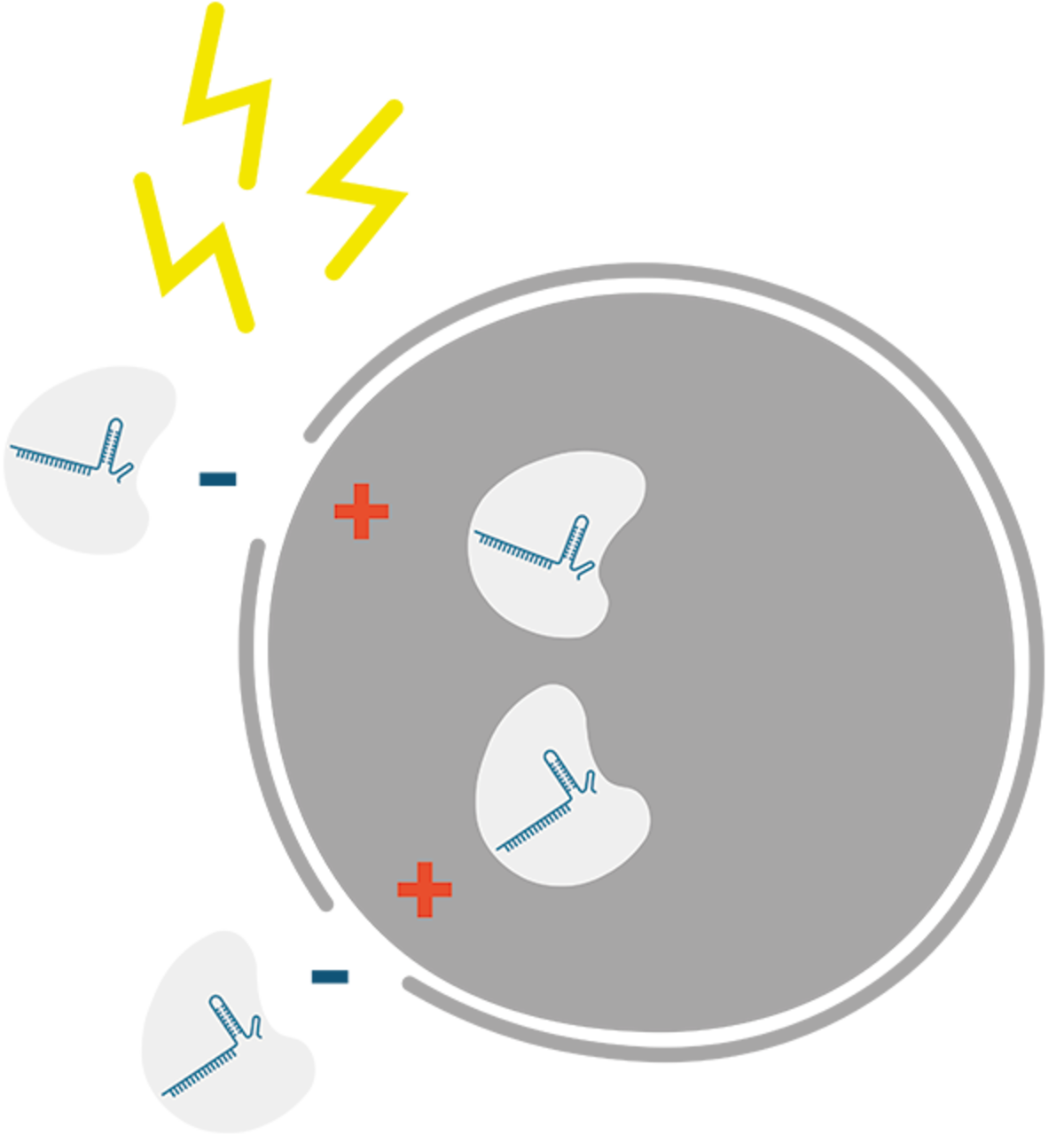
Electroporation enhancers
There are two electroporation enhancers available from IDT. One electroporation enhancer has been developed to work with Cas9 RNP, the other with Cas12a RNP. Both of the electroporation enhancers are single-stranded DNA molecules designed to have no homology to human, mouse, or rat genomes, and are unlikely to incorporate into the genomes of mammalian experimental models. These DNA molecules are thought to act as carrier molecules to improve the rate of RNP delivery into cells during electroporation. This is especially useful if you want to do genome editing in primary cells or cells that are difficult to transfect. Using the appropriate electroporation enhancer brings a great improvement in the efficiency of gene editing, and may reduce the amount of RNP complex required. This, in turn, may reduce the possibility of off-target genome editing and may help improve cell survival.
Important points to consider
The enhancers are only for electroporation, not microinjection or lipofection!
The optimal amount of electroporation enhancer to include differs by the electroporation instrument.
It has been observed that dose-response curves vary for different guide RNA sequences (depending on the potency of the guide RNA). Therefore, IDT recommends titrating the amount of RNP, while keeping the amount of enhancer fixed. Otherwise, toxicity may be observed when using high concentrations of electroporation enhancer.
Transfection by lipofection
In general, electroporation is the method recommended by our supplier IDT. However, if you already have a high-efficiency lipofection protocol for delivering molecules into cells, you may want to try your lipofection protocol for delivery of RNP. Lipofection is primarily suitable for CRISPR experiments in easy-to-transfect cells, such as some adherent, immortalized eukaryotic cell lines. Compared to electroporation, lipofection tends to be cheaper and requires lower levels of RNP. Like electroporation, lipofection usually requires some optimization to suit your cell line. Again, the goal is to minimize cell toxicity and maximize genome editing efficiency. If you are using HEK-293 cells for your CRISPR experiment, the team of scientists at IDT has already prepared an optimized lipofection protocol.
Microinjection (for embryos)
Microinjection is another method of delivering CRISPR components. It is usually used for mouse or rat embryos. In comparison to electroporation and lipofection, it is a labor-intensive, costly, and time-consuming method that requires skilled lab workers and specialized equipment. The main obstacle is that each embryo needs to be injected individually.
In some experiments, electroporation, instead of microinjection, can be an alternative high-throughput method for delivering CRISPR components into embryos. Electroporation removes the need for specialist-handling skills and has less impact on embryo development.
Additional resources
For more detailed information about gene editing using CRISPR-Cas, download IDT's CRISPR basics handbook. Further insights into IDT's products for CRISPR genome engineering can also be found on their website.
Download handbook Go to IDT website Further reading and links
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing, IDT does not intend for these products to be used in clinical applications and does not warrant their fitness or suitability for any clinical diagnostic use. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations.
