Camelid antibodies - Nanobodies - are structurally distinct from conventional IgG antibodies, but function in a similar manner. The antigen binding domains of camelid antibodies, often referred to as nanobodies, are seeing increased use for scientific research due to the many advantages they offer.
How are camelid antibodies different from conventional IgG antibodies?
Camelids (namely camels, llamas, and alpacas) have an immune repertoire of three different IgG subclasses - IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3. Of these, IgG1 is a conventional IgG with two heavy chains and two light chains, whereas IgG2 and IgG3 are heavy chain only antibodies (HcAbs), each comprising two heavy chains that are linked by disulfide bonds. As well as lacking light chains, HcAbs also differ from conventional IgG antibodies in terms of the heavy chain structure. Specifically, while conventional IgG heavy chains have three constant domains (CH1, CH2, and CH3) and a variable domain (VH), HcAbs lack a CH1 domain and are thus smaller.
What are nanobodies?
The term nanobody (used interchangeably with VHH) describes a single heavy chain variable domain of a HcAb. Nanobodies have a molecular weight of approximately 15 kDa, which is about 10-fold smaller than that of a conventional IgG antibody, and bind their antigens monovalently but with equivalent strength to their larger (homobivalent) counterparts. These unique features of nanobodies give them several advantages.
What are the advantages of nanobodies?
A main advantage of nanobodies is that their small size provides better sample penetration, allowing them to bind epitopes that are inaccessible to conventional IgG antibodies. This makes them powerful tools for cellular and in vivo imaging studies such as immunofluorescence, live-cell imaging, or super resolution microscopy, where they offer higher labelling densities, improved resolution, and a reduced risk of adverse immunological reactions.
Nanobodies are also useful for immunoprecipitation experiments. Here, nanobody-based reagents show less background since they circumvent the problem of target proteins being obscured by contaminating antibody heavy and light chains during Western blot detection.
Another important benefit of nanobodies is their superior stability compared to conventional IgG antibodies. Not only can nanobodies withstand fluctuating temperatures, meaning they can be shipped under ambient conditions, but they can also tolerate extreme pH levels and the presence of detergents, salts, and reducing agents in buffers.
In addition, because nanobodies exhibit monovalent binding, they have less of a tendency to form clusters, which can complicate experimental analyses.
Further advantages of nanobodies include greater water solubility and simpler engineering compared to conventional IgG antibodies. Critically, recombinant nanobody production equates to zero batch-to-batch variation, unlimited supply, and the assurance of having a defined sequence.
Lastly, because nanobodies are functionally active without undergoing post-translational modification, they can be produced in bacteria for rapid, cost-effective manufacturing.
How are nanobodies produced?
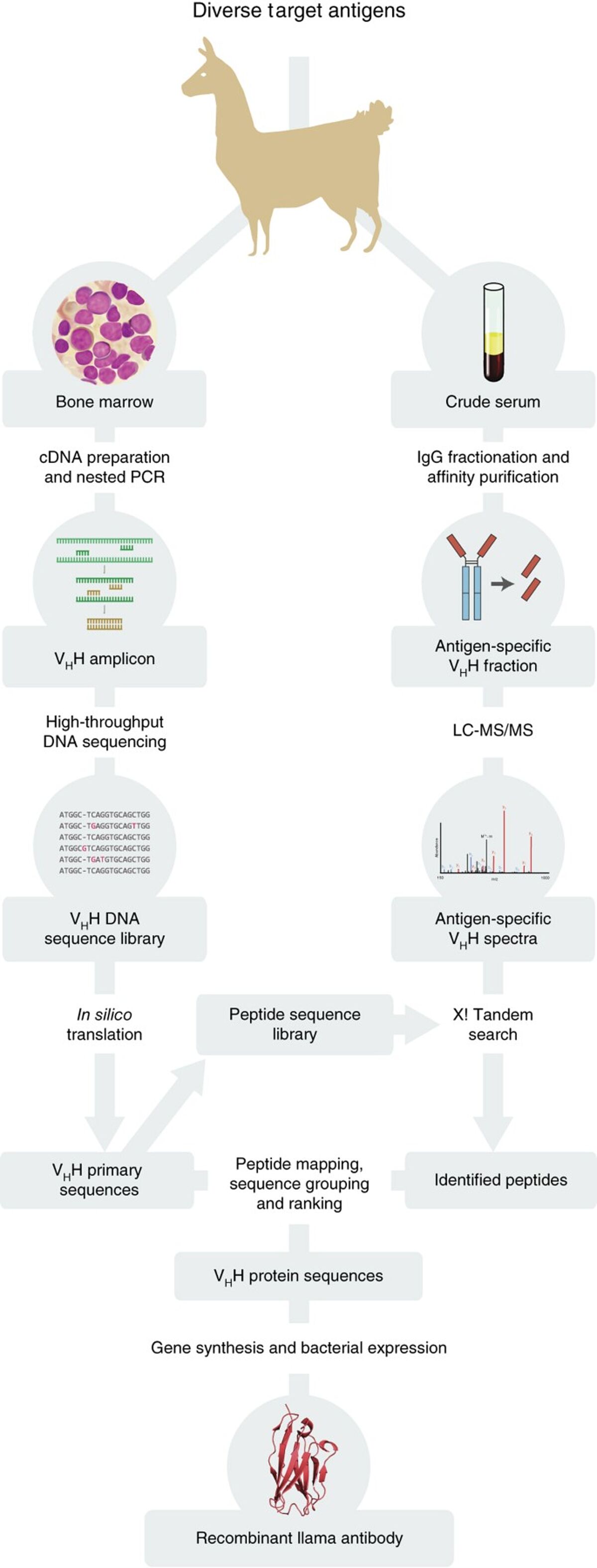
Established methods for nanobody production begin by immunizing a camelid with the antigen of interest. Next, a blood sample is taken, from which the lymphocytes are isolated for mRNA extraction. Following conversion of the mRNA into cDNA and amplification of the VHH gene regions (using primers to conserved HcAb sequences), the nanobodies are cloned for screening by phage display, with techniques such as ELISA being used for identifying the highest affinity binders. Any interesting hits are then transferred into expression vectors for production in a suitable host.
An alternative approach, which avoids the use of animals, involves screening naïve VHH libraries. In addition, some companies offer nanobody development and production services that include engineering a known binding sequence into a nanobody framework.
Figure 2: Overview of nanobody identification and production pipeline - Nature [2]
When should you consider a nanobody development and production service?
Although a growing number of nanobodies is available commercially, including products from ChromoTek and HuaBio, the relative newness of nanobody technology compared to conventional antibody production methods means that relatively few antigenic targets are yet covered. If a nanobody to your protein of interest has not yet been developed, outsourcing its production can be a quick and fairly inexpensive option, especially when compared to the time and cost invested in having a conventional IgG custom made. Companies providing nanobody development and production services include Absolute Antibody, Proteogenix, and QVQ, who are able to adapt their platforms for specific applications.
LubioScience represents some of the most trusted brands in research and works closely with partners including Absolute Antibody, ChromoTek, HuaBio, and QVQ to offer a broad range of nanobody products and services. Contact us today to learn how we can support your project.
More about Lubio’s Antibody development and production services
Suppliers

Absolute Antibody - Recombinant engineered antibodies
Absolute Antibody is an expert in engineering recombinant antibodies for in vivo research. Their custom services include hybridoma sequencing, antibody engineering and expression.

Proteintech - Chromotek - Home of the alpaca antibodies
Proteintech - ChromoTek offers innovative products based on alpaca nanobodies, e.g. GFP-Trap for IP of GFP-fusion proteins, Nano-Secondaries for better IF & more..

QVQ - Single domain antibodies for imaging applications
QVQ develops single domain antibodies for cancer, infectious diseases and age related diseases. Applications include immunofluorescence, cryo-EM and IP.
About QVQ Shop for QVQ products

HUABIO - committed to providing the best antibodies
HUABIO offers recombinant rabbit, monoclonal & polyclonal antibodies of highest quality and carefully validated..

Rapid Novor - focus on the building blocks of life: proteins
Rapid Novor is empowering life science breakthroughs with next generation protein sequencing.
References
- https://www.rapidnovor.com/camelid-antibodies-and-nanobodies/
- Fridy, P., Li, Y., Keegan, S. et al. A robust pipeline for rapid production of versatile nanobody repertoires. Nat Methods 11, 1253–1260 (2014). doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3170