Synthesis of long oligonucleotides: the challenges
The advent of gene synthesis and site directed mutagenesis has driven a need for the synthesis of long oligonucleotides (>75 nucleotides). Despite the demand for these oligos, yields from conventional DNA synthesis and the associated side reactions have historically limited the length of synthetic oligos to <150 nucleotides.
Whilst biological, enzymatic synthesis of DNA has an error rate of just 10-6 – 10-7 (native error rate of proofreading eukaryotic DNA polymerases), chemical synthesis is far less efficient giving a fidelity of only 99% or 10-2 (average coupling efficiency of each nucleoside phosphoramidite). This makes chemical synthesis 10,000 to 100,000-fold less precise and efficient than biological systems. This inefficiency limits standard chemically synthesised oligos to between 5 and 120 nucleotides in length.
A further challenge to the production of long synthetic oligos is that of QC. Mass spectrometry is generally considered the gold standard QC method for oligonucleotide synthesis. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry is effective for 10-50 nucleotides, whilst electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry has a higher accuracy (>0.02%) and can be used for oligos ≤50 nucleotides. Neither however solve the problems presented by long oligos. If a synthesis contains a high proportion of truncated product, they obscure the mass spectra, making it challenging to identify the target species. In addition, natural isotopic variations make peaks broader or less precise for each sequence.
Overcoming the challenges of long oligonucleotide synthesis
Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) have pioneered methods to both synthesise and accurately QC by mass spectrometry oligonucleotides of up to 200 nucleotides in length.
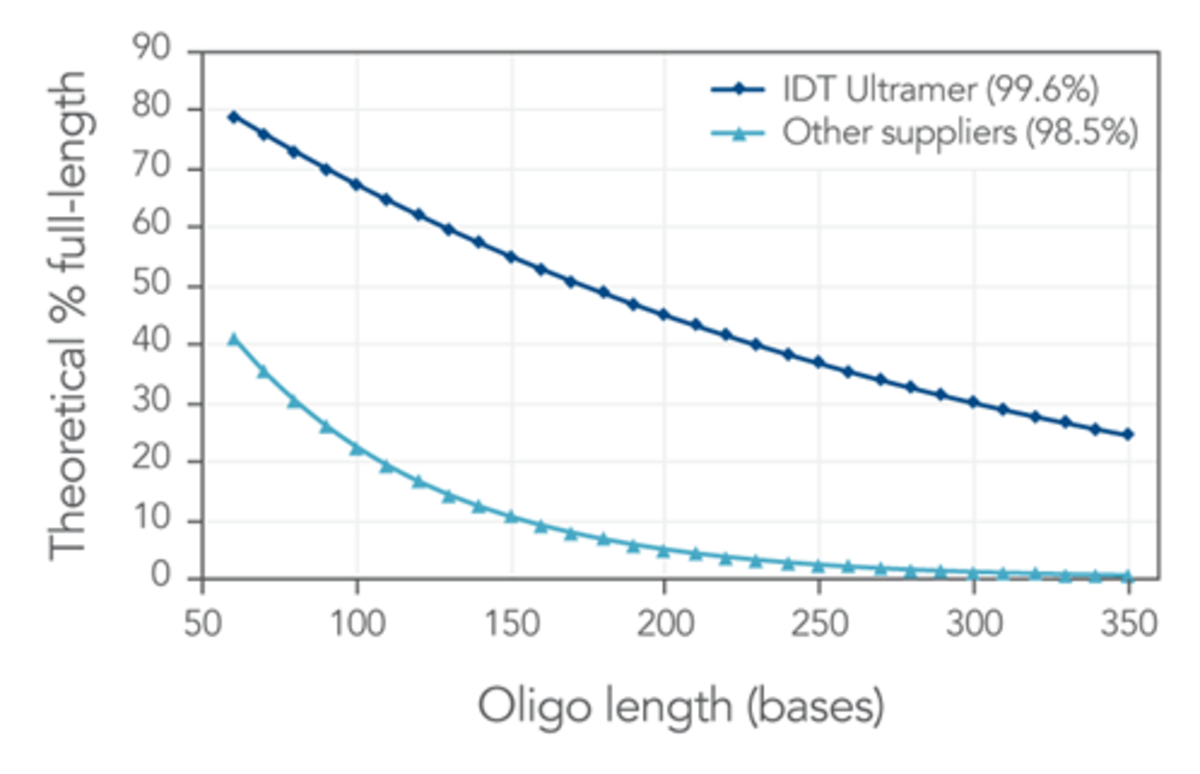
IDT’s long oligos, called Ultramer® Oligonucleotides are synthesised using their proprietary oligonucleotide synthesis equipment. Their platform, when adjusted to a lower throughput mode, which uses an ‘extra rich synthesis cycle for long oligos, permits high-quality synthesis of oligos up to 200 nucleotides in length. Their chemistry has an average coupling efficiency of >99.5% through the entire 200-base synthesis (Figure 1). In addition to their proprietary processes, they have developed a unique solid support, which permits synthesis of low-yield, high quality oligos of lengths greater than 200 nucleotides.
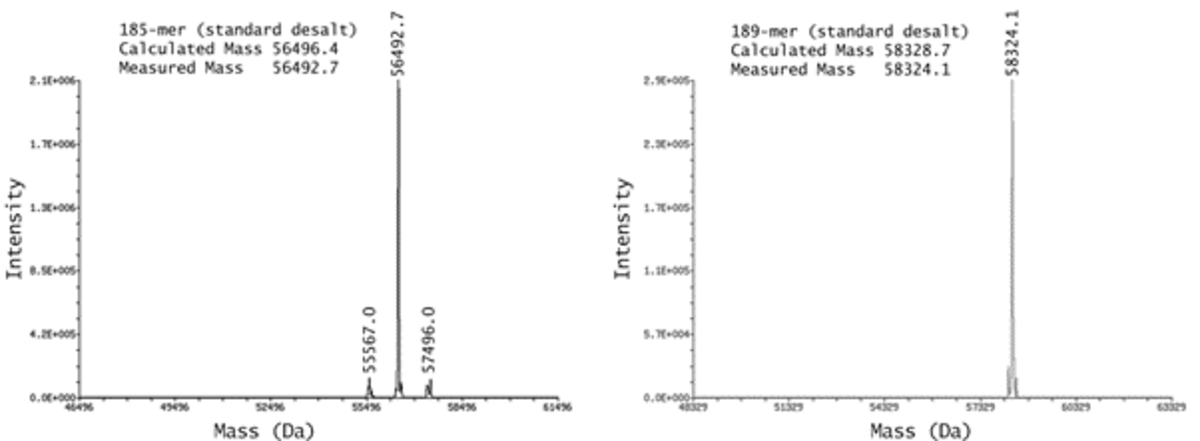
IDT’s proprietary mass spectrometry facilitated their ability to offer oligos of up to 200 nucleotides with the surety of ESI documentation as a guarantee of purity to their customers (Figure 2). QC data shows high purity of 185 and 189 nucleotide Ultramer® DNA Oligos. The measured molecular weight of each oligo is within 0.01% of its expected molecular weight. Data generated from IDT in-house ESI-MS instruments.
Applications for ultralong oligos
- Site-directed mutagenesis – efficiently and quickly generate large insertions, deletions or change stretches of sequence identity.
- Templates for in vitro transcription – templates for RNA synthesis
- ddRNAi – hairpins cloned into an expression vector
- Homology-directed repair
- Gene-construction and cloning – CRISPR genome editing as HDR templates
- shRNA library prep
- Targeted resequencing
Ultramer® oligonucleotides
Available single- or double-stranded and can be delivered in tubes or plates.
- Complete confidence in oligos that are verified by electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (EIS).
- Unrivalled control of oligo specifications with custom formulation and mixing options
| Description | 200 pmol Ultramer | 4 nmol Ultramer | 20 nmol Ultramer | PAGE Ultramer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avaliable formats | Plates | Plates & tubes | Plates & tubes | Tubes |
| 5' Phosphorylation | * | * | * | * |
| 5' Biotin | * | * | * | * |
| 5' Amino Modifier C6 | * | * | * | |
| 5' Amino Modifier C12 | * | * | * | * |
| 5’ Deoxylnosine | * | * | * | * |
| 5’ DeoxyUridine | * | * | * | * |
| Int deoxyInosine | * | * | * | * |
| Int deoxyUridine | * | * | * | * |
| Phosphorothioate Bond | * | * | * | * |
| 2’ O-Methyl RNA bases | * | * | * | * |
| 3’ Amino Modifier | * | * | ||
| 5’5-Methyl dC | * | * | * | |
| Int 5-Methyl dC | * | * | * | |
| Int Spacer 18 | * | * | * | |
| 3’ C3 Spacer | * | * | * |